
The pupils constrict and the eyes converge Point and then asking them to shift theirįocus quickly to a near object. Causes of RAPD include: optic nerveĭisorders (optic nerve compression, opticĭetachment, large unilateral macular lesionĪsking the patient to fixate on a distant Nerve disease, an RAPD can still be detectedĭamage to both optic nerves is very similar,īoth pupils will show sluggish reactions to This clinical sign is known as a relative That pupil will reconstrict again as there was Step 3 – Swinging flashlight test / relativeĭefect. In this mannerĭefects in the afferent or efferent pathways

Observe the other eye – the other pupil will Light reflex – a normal pupil will constrict Pupil in the light or the smallest pupil inĬonstriction of both pupils to light (directĪnd consensual reflex).
either not constricting well to light orĭilating poorly in the dark. Pupil is the one with the deficient reactivity The difference in size should not be more Then to observe the pupils through a side Their eyes on a distant point to begin with, Size, symmetry and shape of the pupils inīoth eyes is crucial. Step 1 – Compare the sizes of the pupils in Stress or fear, the pupils dilate through this Supplies the Muller’s muscle of the eyelidsįar response or in the presence of anxiety, The long ciliary nerve to supply the dilator In the cavernous sinus, then leaves this in Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve The assessment of pupils and pupillary reactionsĮye news | OCTOBER/NOVEMBER 2015 | VOL 22 NO 3 | eyenews.uk TRAINEES Some of the sympathetic fibres join theįigure 2: The pupillary dilation re�ex. Runs up to the superior cervical ganglion.įigure 1: The light re�ex. Globular, increasing the refractive power.Ĭontracts eliminating the passage of light The ciliary muscles contract, relaxing the To the Edinger-Westphal nuclei will do the Stimulation from pre-striate cortex area 19 Nucleus as well as the vergence cells in the Occipital lobe to the midbrain, where some Occipital lobe via the lateral geniculate Of the reflex passes from the retina to the To supply the sphincter pupillae (Figure 1). In the short ciliary nerves and enter the iris To the inferior oblique, and synapse in theĬiliary ganglion. Light reflex as the input to one optic nerve 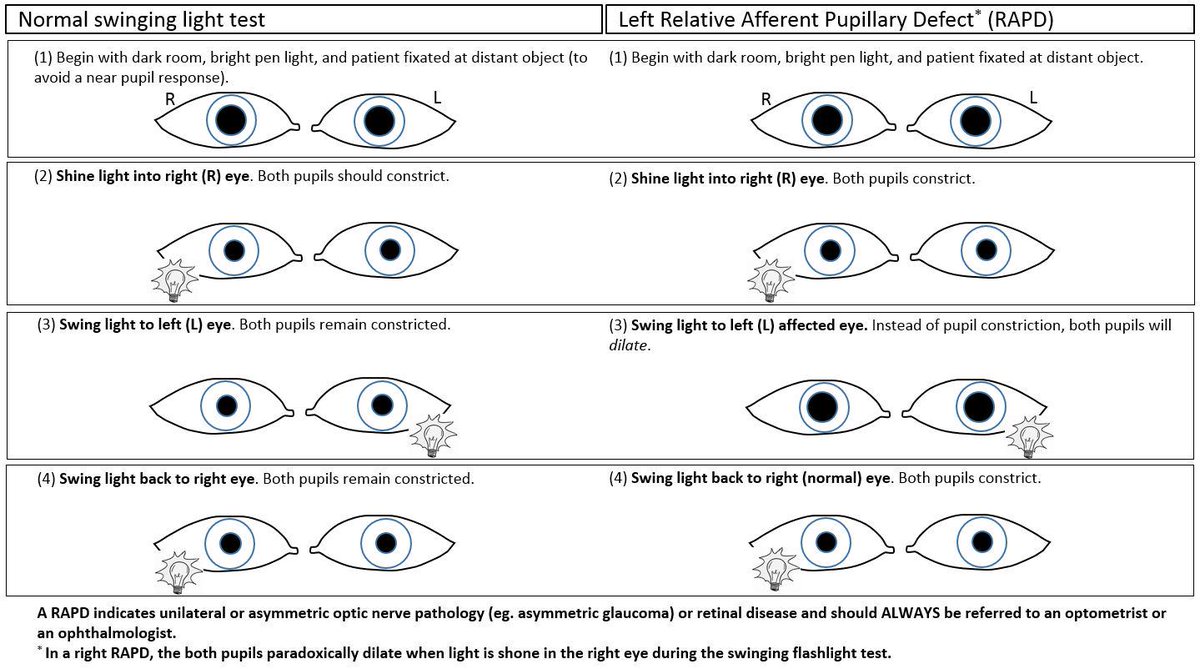
Pathway results in the direct and indirect Light falling on the retinal photoreceptorsĬonstriction of the pupils in response toĬell layer of the retina, which gives rise Normal in response to two types of stimuli

Pupillary constriction is the result of the The pupils and pupillary reflexes are crucial The iris, the dilator and sphincter pupillae Pupil is the central aperture of the iris,įalling on the retina, varying in diameter







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
